
The Princess and Curdie by George MacDonald, 1883.
This is the sequel to The Princess and the Goblin, but it isn’t as well-known. Personally, I prefer The Princess and the Goblin, but it’s worth explaining what this book is like and how this two-book series ends.
When we last met Curdie, he was living in a cottage in the mountains and working in the mine with his father. At the beginning of this story, he is still there and still working in the mine. Most of the goblins who inhabited the mines were drowned at the end of the previous book. The beginning of the story briefly recounts the previous adventure and how the king offered Curdie a position in his guard after he helped to rescue the princess and fight the goblins. Curdie turned down the position to remain with his parents, and the king accepted his decision because he approved of the boy’s loyalty to his family. Since then, the king took Princess Irene away with him, and Curdie has missed her.
Since the old, castle-like manor house where the princess spent her earliest years flooded at the end of the story, Curdie has wondered what happened to the great-great-grandmother the princess always spoke of. Nobody ever saw her leave the house, but then again, nobody but the princess and her father ever saw her at all. Curdie’s mother says that she once saw a mysterious light, like the kind Princess Irene said that her great-great-grandmother had, but Curdie still thinks maybe the princess just dreamed that she had a great-great-grandmother, even though he once followed the magical string that the great-great-grandmother gave her.
As Curdie grows up, he believes in fewer things than he once did and focuses more on being a miner than on the little things he once noticed in the upper world. The book describes him as becoming mentally dull and more rigid and common in his thinking. Like other common and mentally-dull people, he is starting to follow the path of being so afraid of being fooled into believing something foolish that he is at risk of making a fool of himself because he is unable or unwilling to think about things deeply, consider possibilities, and believe things that he should:
“There is this difference between the growth of some human beings and that of others: in the one case it is a continuous dying, in the other a continuous resurrection. One of the latter sort comes at length to know at once whether a thing is true the moment it comes before him; one of the former class grows more and more afraid of being taken in, so afraid of it that he takes himself in altogether, and comes at length to believe in nothing but his dinner: to be sure of a thing with him is to have it between his teeth. Curdie was not in a very good way then at that time.”
Curdie’s parents worry about this change in him and find themselves wistfully thinking about how he was when he was younger. Curdie no longer makes up the songs and verses he used to because it is no longer necessary to scare the goblins away. He seems to have lost much of his former creativity, imagination, and mental flexibility because he has not been exercising them, and with them, he has been losing his critical-thinking and analysis skills and his ability to look outward and see the big picture of life and other people.
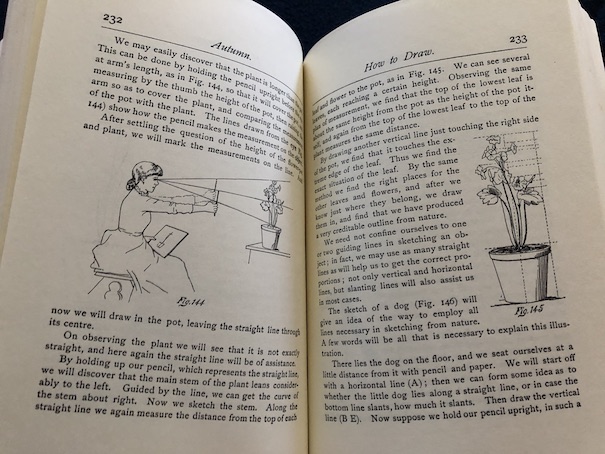
One day, Curdie makes a bow and arrows, and he uses them to shoot a pigeon. As he watches it die, he is horrified at what he has done. He suddenly remembers what the princess said about her great-great-grandmother keeping pigeons, and he feels terrible that he has killed something so lovely. His remorse stirs his heart and brings back the memories and feelings of the boy he used to be. Then, the pigeon moves, and he realizes that it is still alive, and he sees the globe of light of the great-great-grandmother. Curdie hurriedly takes the injured pigeon to the old castle. The door is open, so he goes inside and follows the sound of a spinning wheel to find the princess’s great-great-grandmother, seeing her for the first time.
Curdie admits what he has done to the great-great-grandmother and gives her the bird. The two of them discuss right and wrong, and Curdie comes to realize that he has done a great many wrong things for some time because “I was doing the wrong of never wanting or trying to be better. And now I see that I have been letting things go as they would for a long time. Whatever came into my head I did, and whatever didn’t come into my head I didn’t do.” In other words, Curdie has fallen into the habit of being thoughtless, and this is the first time in a long time that he’s paused to think about things he’s been doing or could have been doing instead. He realizes that he has even been grumbling about his work and not adequately helping his parents, and even though he noticed that they’ve been seeming unhappy and he suspected it had to do with him, he never once asked them how they felt or why.
After they have this talk and Curdie realizes the real problems behind the things he’s done and is genuinely sorry for them, the lady tells him not to worry because the pigeon will recover now, and she will take care of it. She merely gives him the caution to “Do better, and grow better, and be better. And never kill anything without a good reason for it.” Curdie offers to destroy his bow and arrows, but the lady tells him not to because there are bad things that need to be killed and that the bow and arrows may be useful someday. She also tells him that there are people who tell stories about her and laugh about her, and she asks that Curdie not laugh with them or side with them.

Curdie goes home and tells his parents what happened. They believe him and say that he should do what the lady says. The next day, when the other miners are telling stories about the lady, saying that she’s an evil witch, Curdie has to fight to hold his tongue. When they press him for what he thinks, he only says that he thinks that, if they’re going to tell stories about her, they’d better be sure that they’re true because she wouldn’t like to be slandered. The others laugh at him for being afraid of her or for wanting to defend her.
The lady appears to Curdie and his father again later. She tells them that they have the blood of the royal family in their veins, and she hints that there is a special destiny in store for Curdie. Curdie tries to ask her some questions about who she really is and about her changing appearance, but all she says is that she has many names and can appear in many different forms, and even different people see her differently. She tells Curdie to come see her alone in her tower the next night.
When he sees her the next time, the lady asks if he is ready for a difficult trial. She says that it will hurt and that it will require trust and obedience, but it will be good for him. When Curdie tells her to command him, she tells him to put both of his hands into her fire. He does it quickly, trying not to think about it, and it does hurt at first. However, it stops hurting, and when he takes his hands out of the fire again, he discovers that they are softer than they were before. The roughness and callouses from his work in the mines are gone. The lady tells him that his hands have changed more than that. She says that he will now be able to feel when he touches the hand of a man who is actually a beast on the inside, but he will lose that gift if he uses it for a selfish purpose. To demonstrate the gift, the lady calls a strange creature called Lina to them, and when Curdie feels the creature’s paw, it feels like a child’s hand. Although the creature appears strange and menacing, it’s actually good and gentle on the inside.
The lady tells Curdie to tell his parents that he must go to the king’s court the next day. She has given his father an emerald that they can use to see if he is all right during his travels because its appearance will change if he isn’t. The lady also sends Lina with Curdie to help him on his journey. Curdie is a little uneasy about that because he can tell that Lina is one of the goblins’ creatures, but Lina is genuinely helpful to him, and he becomes fond of her.

When they finally reach the king’s city, Curdie meets the king’s baker. The baker stumbles on a stone sticking up out the street and curses the king for not maintaining that road. Curdie argues that the baker himself bears some responsibility for watching where he’s going, especially since he says that he’s tripped on that stone before and knows it’s there. However, Curdie has his pickaxe with him and sees an easy way of dealing with the problem. He breaks up the rock that’s sticking out of the road, but a piece of it flies out and breaks the barber’s window. The barber comes to complain about it, and he insists that Curdie pay him more than the window is actually worth. Curdie gives him what he thinks is a fair price, and he feels the animal paw in the barber’s hand, showing what kind of man the barber is and that Curdie’s gift is still working.
There are other cruel, hard-hearted, immoral, and brutish people in this city, and sadly, some of the nicer people tend to be on the receiving end of the malicious gossip of the others. Curdie and Lina are taken in by a woman who is rumored to be a witch simply because she prefers to live quietly and not gossip like the others. Of course, everyone immediately begins gossiping about Curdie and his strange animal companion. The local magistrate believes the slander of a couple of people whose dogs Curdie had to kill because they were trying to kill him and Lina. These people claim that the dogs were harmless and Curdie killed them for no reason. When the magistrate and his soldiers come to arrest Curdie, he says that he’ll surrender, but he refuses to restrain Lina so they can kill her. Lina chases off the crowd that’s gathered to watch, but then, she vanishes herself, and Curdie is arrested. Fortunately, Curdie manages to escape and reunite with Lina. Then, he and Lina find their way into the king’s cellar and kitchen. There, he finds that the king’s servants are drunk and passed out. His touch tells him that these people are beasts inside. Going further into the palace, he finds the king’s chamber, and there, he meets Princess Irene again.
Princess Irene recognizes Curdie again immediately. It’s been less than two years since they last saw each other. She was about eight years old then, so she can’t be more than ten years old now, but Princess Irene seems older than she should be because of everything that’s been happening in the king’s palace. Her father has been ill for a year and is not in his right mind. Princess Irene thinks that the entire kingdom is concerned for him because that’s what the lord chancellor has told her, but Curdie knows that isn’t true because he hasn’t heard a word about there being anything wrong with the king outside of the palace. Princess Irene says that the king has also asked for Curdie, and his staff claimed that they tried to send for him but couldn’t find him. Curdie knows that definitely isn’t true because, until he started his journey to the king’s palace, he had been living in the same cottage where he always lived, and no one from the palace tried to find him or sent him any message.
It’s obvious that there are wicked people in the palace. These people are responsible for the king’s current condition, and they’re trying to keep the public from finding out what’s been happening. With his gift of telling who is a beast on the inside, can Curdie help Princess Irene to find and deal with the conspirators and restore the king to his right mind?
The book is public domain now. It is available to read online through Project Gutenberg (multiple formats) and Internet Archive (multiple copies). You can also listen to a LibriVox audio reading online through YouTube or Internet Archive.
My Reaction and Spoilers
As with the first book, royalty is used to represent people with the best morality in the story. Curdie and his family have royal blood because they are more wise and moral than other people around them. It feels a bit classist to think that royalty is supposed to be morally superior to everyone else just because they were born into a particular family. That certainly isn’t how these things work in real life. Just think of Prince Andrew. However, this type of comparison does fit with the fairy-tale setting of the story.
In spite of whatever royal blood he has, Curdie isn’t perfect. He was falling into bad habits until he realizes that he has done a terrible thing by shooting the pigeon, which causes him to seek out the great-great-grandmother Princess Irene told him about and to do some soul-searching about his behavior. During the time when Curdie is being thoughtless and falling into bad habits, he is portrayed as being too common, like the other men working in the mine. However, I would argue that the bad habits of the miners, like their wild, gossipy stories and rude joking and teasing, are not because they lack royal blood but because they lack thought. Curdie and his father say as much when they’re talking in the mine. The other miners are being thoughtless, and they’re simply not making any effort to be more thoughtful. More than any royal blood, Curdie proves himself worthy by his ability to be thoughtful about other people, and he gets that ability by wanting to improve himself and making the effort to do what it takes to improve.
A large part of this book comes off as a lecture about morality, but that’s not unusual for a Victorian era children’s book. The Princess and the Goblin had some of that, too, but this book has much more. That might be part of the reason why this book seems like it’s less well-known than the first book, but the ending of the book is also strange and kind of depressing.
As one might expect in a fairy-tale story of this kind, Princess Irene marries Curdie (not immediately, because they’re still children, but eventually), and the two of them are said to rule their kingdom wisely for many years. It seems like a happy ending because, thanks to Curdie’s ability to sense the true nature of people, they are able to surround themselves with the best people, and the city becomes less wicked under their rule. However, the story doesn’t end there. In the final paragraphs of the book, it says that Curdie and Irene had no children to inherit the crown. Without a blood heir to the kingdom, someone else was chosen to rule instead, and this person was wicked and greedy, so the royal city went back to being wicked. In fact, this new king was so greedy and stupid that he had his people mining continuously, right under the city itself, to bring him riches. They eventually completely undermined the entire city, so the city physically collapsed in on itself, destroying it completely and killing everyone there. I guess that’s meant to explain why this fairy tale kingdom no longer exists, but that’s quite an ending to this story! With this royal family apparently having some kind of magic about them, it seems incredible that their kingdom would have gone this way, but then again, maybe the author just didn’t want to write about them anymore.
Note to the wise: Wherever your source of wealth comes from, for the love of all that is good in the world, don’t mine your support beams! They serve a purpose and need to stay there for a reason.





























 Toby Tyler; Or, Ten Weeks with a Circus by James Otis, 1881.
Toby Tyler; Or, Ten Weeks with a Circus by James Otis, 1881. Toby think that it sounds like an exciting offer, and Mr. Lord persuades Toby that the best way would be for him to sneak away at night because his Uncle Daniel might disapprove and stop him from taking the job. Not taking that as a warning, Toby agrees. Toby feels a little guilty about running away and surprisingly homesick, but he decides to stand by the agreement he made with Mr. Lord and see what possibilities life with the circus might have for him.
Toby think that it sounds like an exciting offer, and Mr. Lord persuades Toby that the best way would be for him to sneak away at night because his Uncle Daniel might disapprove and stop him from taking the job. Not taking that as a warning, Toby agrees. Toby feels a little guilty about running away and surprisingly homesick, but he decides to stand by the agreement he made with Mr. Lord and see what possibilities life with the circus might have for him.