Thank You, Mr. Falker by Patricia Polacco, 1998.

When little Trisha turns five years old, her grandfather introduces to her to reading in the same way he has done for other children in the family, with a taste of honey on a book, to remind her that knowledge is sweet. Trisha already loves books because her mother reads to her every night, and other members of the family also read to her. She’s looking forward to learning to read herself.
However, when she starts going to school, she finds that she has trouble learning to read. She likes drawing, and other kids at school admire her drawings, but for some reason, she struggles at deciphering the letters that other kids seem to learn so easily. When she looks at writing on a page, everything looks like wiggling shapes, and she has trouble figuring out what sounds they’re supposed to make. Other children move forward with their reading lessons, but Trisha struggles and starts to feel dumb.


Trisha asks her grandmother if she thinks she’s different from the other kids, and her grandmother says that everyone is different and that’s “the miracle of life.” Trisha asks if she thinks she’s smart, and her grandmother says she is. That makes her feel a little better, but why can’t she read like the other kids?
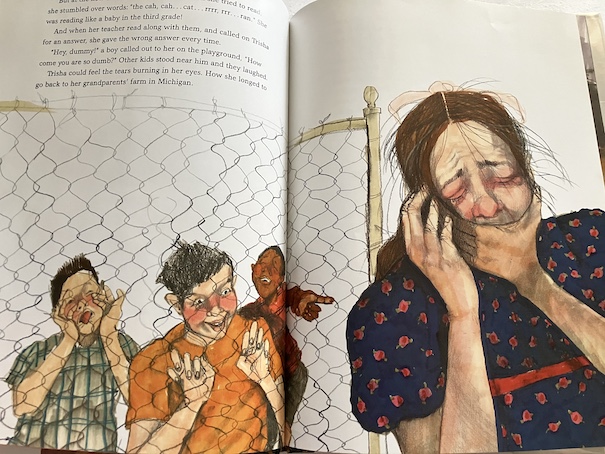

Trisha continues to struggle in school, even after the family moves from Michigan to California. She is in third grade at that point, and other children insult her and tease her when she struggles, and Trisha feels dumber than ever. She spends more time drawing and daydreaming, and she starts hating school, sometimes pretending that she’s sick so she won’t have to go.

Things only start to improve for her in fifth grade, when she gets a new teacher, Mr. Falker. Mr. Falker doesn’t cater to the teacher’s pets like other teachers do, and he notices Trisha’s artistic talent and praises her for it. He also stops the other kids from teasing Trisha in class when she struggles, although one boy, Eric, continues to bully Trisha terribly and get other kids to gang up on her when the teacher isn’t looking until Mr. Falker finally catches him.
Mr. Falker works with Trisha to improve her reading and reassures her that she is not stupid. He realizes that the reason she has struggled with reading is that Trisha doesn’t see letters the way other kids do, and he points out that she’s actually been clever in the way she’s managed to hide just how much she’s been struggling all this time.


Mr. Falker introduces Trisha to Miss Plessy, a reading teacher, and the two of them work with her to develop techniques that improve her reading skills. Gradually, Trisha begins to make real progress, and she begins to feel the sweetness of knowledge that her grandfather talked about.
The book is available to borrow and read for free online through Internet Archive.
My Reaction
The end of the book explains that the story is autobiographical. Patricia Polacco was the Trisha in the story, and she did have trouble learning to read until the read Mr. Falker realized how she was struggling and helped her. At the end of the story, the author says that she met Mr. Falker again years later and thanked him, telling him that she can become a children’s author.
There is a difference between real life and the story, though. In the book, Trisha is in the fifth grade when she gets help with her reading, but in real life, Patricia Polacco was apparently 14 years old and in junior high school. The book doesn’t say exactly what the cause of Trisha’s learning difficulties is, but she is apparently dyslexic, based on the description and because Patricia Polacco was dyslexic in real life.
I enjoyed seeing this part of the author’s childhood, although I found the part with the school bullies stressful. I do think it was important to include that part, though, because that can be part of the experience of children who struggle in school. Although Eric is an obvious bully in the story, the other kids also make Trisha miserable with their teasing and insults. It occurred to me that they may not all think of themselves as bullies, but at the same time, a person doesn’t have to think of themselves a bully in order to be one. Bullying is a behavior, and it exists independently of self-identity. Part of me wondered, if the girl and the teacher in the story are both real, were the bullies also real, and if so, did any of them ever read this story and recognize themselves? Maybe some did, and maybe they didn’t. Maybe not all of them would even care, if they had.
Regardless, I do think stories like this can be useful as a preemptive measure against bullying by showing kids how their behavior can affect other people and what may be going on in the life of a person they’re teasing or bullying. While I’m sure that everyone thinks of themselves as being the heroes of their own story, I think people sometimes need a reminder that, at the very same time, they are also supporting characters in everyone else’s story, for good or bad. In a way, we’re all self-casting in every story we’re in by the ways we choose to act as we go through life’s story in general.
The bully antagonists aren’t really the main focus of the story, though. They act as further obstacles to the problem that Trisha is trying to solve, but ultimately, the story is really one of gratitude toward the teacher. Part of what the teacher does for Trisha is to shut down the bullies so Trisha can focus on what she needs to learn and he can focus on helping her. Even more importantly, Mr. Falker helps Trisha to see that she is smart and capable. It takes a little more work for her to make progress than others because she has a condition to overcome, but with a little help, she can do it. It really opens up a whole new world for her, and she finally gets to taste that sweetness that comes with knowledge.

I’ve heard of the tradition of giving children a taste of honey before they begin their lessons. When I was a student, I thought I remembered a teacher mentioning this tradition to us as a Greek tradition. It might be, although when I tried to look it up, I couldn’t find anything about Greece. I found references to it as a Jewish tradition, which would make sense for Patricia Polacco’s family.
Patricia Polacco’s real-life grandmother also appears in the story, the same grandmother who appears in another of Polacco’s books, Thunder Cake. Her grandfather wasn’t present in that story, but he is in this one. Both of the grandparents are mentioned as dying before the story ends.